In the evolving landscape of IT, virtualization tools have become indispensable. They enable IT professionals to maximize resources, reduce hardware costs, and simplify system management. With a multitude of options available, it can be challenging to determine which tools suit your specific needs.
This article explores into some of the best virtualization tools available, highlighting their features and benefits to help IT professionals make informed decisions.
1. VMware vSphere
VMware vSphere stands out as one of the most widely adopted virtualization platforms. It offers a comprehensive suite of tools tailored for server virtualization, making it an excellent choice for enterprises requiring high scalability and robust performance.
Its vMotion technology enables seamless virtual machine migration, while advanced resource management optimizes CPU, memory, and storage utilization. Moreover, integration with other VMware products creates a unified IT environment, ensuring streamlined operations. Though reliable and backed by extensive support, VMware vSphere’s higher cost can be a barrier for smaller organizations, making it more suitable for enterprise-level environments.
2. Microsoft Hyper-V
Microsoft Hyper-V is another strong contender in the virtualization market, particularly for businesses already embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem. It integrates seamlessly with Windows Server and Azure, providing an intuitive and efficient virtualization experience.
Key features such as live migration, built-in backup and recovery, and support for diverse guest operating systems make Hyper-V a practical and cost-effective solution for Windows-centric infrastructures. However, while Hyper-V offers excellent value for its price, it may lack certain advanced features found in competing platforms like VMware, potentially limiting its appeal for some enterprises.

3. Oracle VM VirtualBox
Oracle VM VirtualBox is a popular free and open-source virtualization tool known for its simplicity and flexibility. Its cross-platform support enables it to run on operating systems like Windows, macOS, Linux, and Solaris, making it a versatile choice for developers and small to medium-sized businesses. Features such as snapshot capabilities and support for various guest operating systems enhance its functionality, while extension packs provide additional capabilities.
While VirtualBox is lightweight and easy to set up, its lack of enterprise-grade features makes it more suitable for individual developers or smaller-scale implementations.

4. Citrix Hypervisor (formerly XenServer)
Citrix Hypervisor, formerly known as XenServer, is tailored for enterprise environments that demand high performance and scalability. With features like advanced GPU virtualization, dynamic workload balancing, and robust disaster recovery, it is particularly well-suited for organizations focusing on virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) and application delivery.
Integration with Citrix Workspace further enhances its capabilities in VDI solutions. While Citrix Hypervisor offers competitive pricing and strong support for graphical workloads, its ecosystem is smaller compared to VMware, which may limit its adoption in broader use cases.

5. Red Hat Virtualization (RHV)
Red Hat Virtualization (RHV), built on the Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM), offers a cost-effective open-source solution for enterprises. It integrates seamlessly with Red Hat OpenStack and Ansible, providing advanced management tools for virtualized environments.
Known for its high performance and scalability, RHV is ideal for Linux-based infrastructures and businesses leveraging open-source ecosystems. While its cost-effectiveness and flexibility are significant advantages, the platform’s less user-friendly interface compared to proprietary solutions may pose a challenge for newcomers or businesses without dedicated technical expertise.
6. Proxmox Virtual Environment
Proxmox Virtual Environment (Proxmox VE) is a powerful open-source platform that combines KVM for virtual machines and LXC for containers. Its web-based interface enables centralized management, while clustering capabilities ensure high availability for critical workloads. With built-in backup and recovery tools and support for ZFS, Proxmox VE offers advanced storage management.
These features make it an attractive option for small to medium-sized businesses and open-source enthusiasts. However, its limited commercial support compared to enterprise-grade platforms may deter organizations requiring extensive professional services.
7. Nutanix AHV
Nutanix AHV is a hypervisor designed specifically for the Nutanix hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) platform. By eliminating the need for standalone software, it simplifies virtualization and reduces overhead. Nutanix AHV provides centralized management through a single interface and offers high performance, making it an excellent choice for organizations adopting HCI.
However, its reliance on Nutanix infrastructure limits its use as a standalone solution, which may not suit businesses seeking a more flexible or independent virtualization tool.
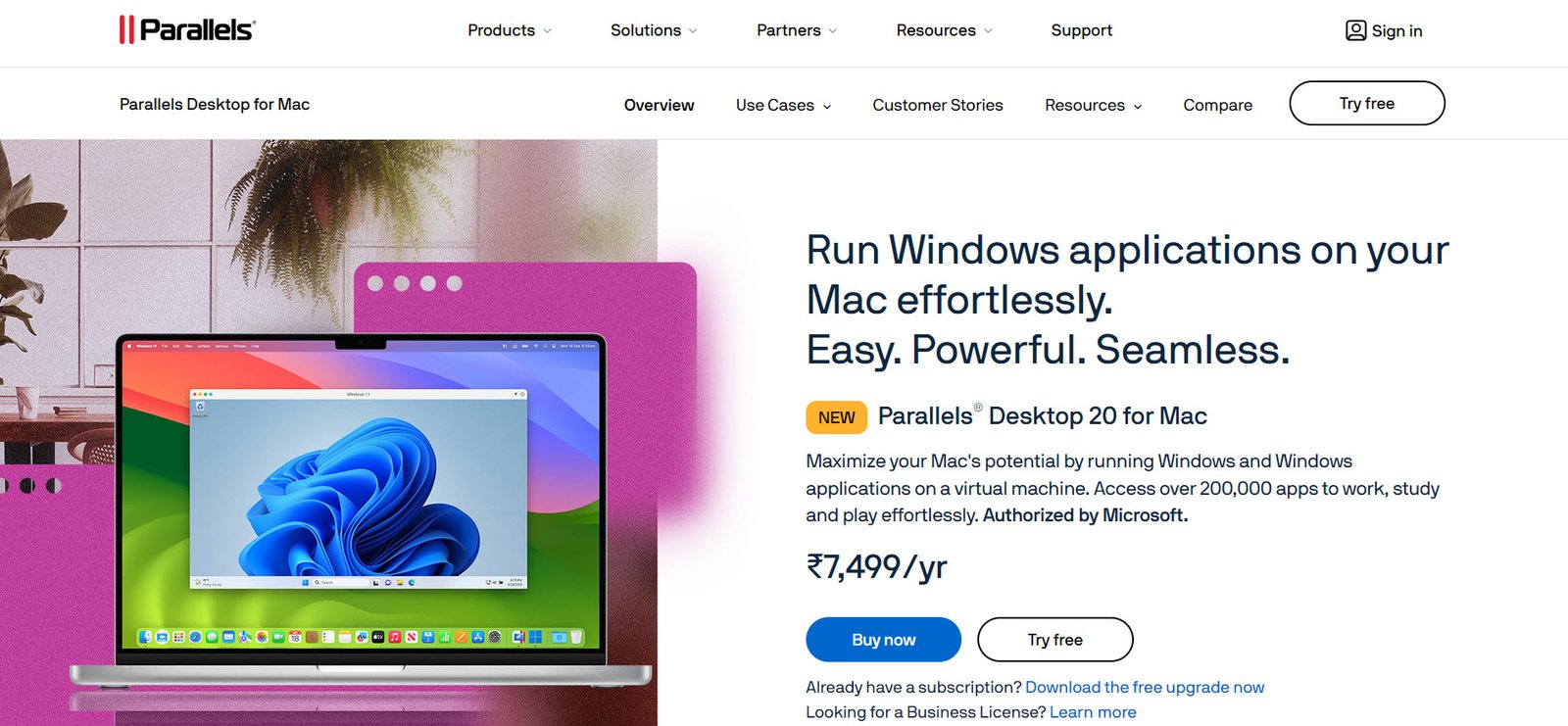
8. Parallels Desktop
Parallels Desktop is a virtualization tool designed for macOS users who need to run Windows or Linux applications seamlessly. With its intuitive interface and optimization for macOS, Parallels Desktop enables users to run Windows apps alongside macOS apps through its Coherence mode. It also integrates well with popular developer tools, making it an excellent option for macOS users and developers.
While Parallels Desktop offers exceptional performance and user-friendliness, its compatibility is limited to macOS environments, restricting its use for organizations relying on other operating systems.
Conclusion
The best virtualization tool depends on your specific requirements, budget, and infrastructure. For enterprises seeking advanced features, VMware vSphere or Citrix Hypervisor may be ideal. Developers and small businesses might prefer Oracle VM VirtualBox or Proxmox VE for their cost-effectiveness and simplicity.
For organizations already invested in a specific ecosystem, tools like Microsoft Hyper-V or Nutanix AHV offer seamless integration.
By carefully evaluating your needs and the features of each tool, you can select a virtualization platform that enhances productivity and supports your IT infrastructure goals.



